Pythagoras
Theorem:
Case-I (At Right Angle) Case-II (At Acute Angle) Case-III (At ObtuseAngle)
a2 = b2 + c2 a2 < b2 + c2 a2 > b2 + c2
The possible quant-comparison Q’s for GRE:
Each question from Q1 to Q5 consists of two quantities, one in column A and one in column B.
You are to compare
the two quantities and choose
A if the quantity in column A is
greater;
B if the quantity in column B is
greater;
C if the quantities are equal;
D if the relationship cannot be
determined from the information given;
A 20 foot ladder
leaning against a vertical wall with the base of the ladder 10 feet
from wall is pulled 2
feet farther from the wall causing the top of the ladder to
drop x feet.
Column A Column
B
X 2
Solution:
Consider right
triangle ABC. Let BE = y
Applying Pythagoras
theorem at angle B,
(x+y)2 +
102 = 202
(x+y)2 = 400 – 100 = 300 - -> (1)
Consider right
triangle ABC. Let BE = y
Applying Pythagoras
theorem at angle B,
y2 + 122
= 202
y2 = 400 –
144 = 256 => y = √256 = 16 - -> (2)
Substituting value of
y from (2) in (1),
(x+16)2 =
300 => x+16 = √300 => x = √300 – 16
√300 value lies
between 17 and 18 (as 172 = 289 and 182 = 324)
Hence x value lies between
(17-16) and (18-16) ie., 1 and 2
and must be less than
2. Hence answer option is “A”
Q2) Column A Column B
AB2 + BC2 AC2
Solution:
This is a tricky
question. Don’t take it granted that ÐB is 90.
As we have no clues
about ÐB or lengths of the sides,
we could not find the
relationship between the given columns.
Hence answer option
is “D”
Q3) Column A Column B
X z
Solution:
Observe that ÐB = 90,
Applying Pythagoras theorem
at B, z2 = x2 + y2 => z > x
And hence answer
option is “B”

Q4) Column A Column B
ÐB 900
Solution:
AC2 = 252
= 625; AB2 = 202 = 400; BC2 = 152 =
225
Observe that AC2
= AB2 + BC2, hence ÐB = 90
And hence answer option is “C”
ÐB 900
Solution:
AC2 = 252
= 625; AB2 = 222 = 484; BC2 = 152 =
225
AB2 + BC2
= 484+225 = 709
Observe that AC2
< AB2 + BC2, hence ÐB < 900
And hence answer
option is “A”
Q6 consists
of a mathematical problem, and 2 statements containing data.
Then you
have to choose one of the 5 different answer choices regarding
which of the
2 statements is sufficient for you to answer the problem.
The answers
will be:
A. Statement 1 ALONE is sufficient but statement 2 alone
is not sufficient.
B. Statement 2 ALONE is sufficient but statement 1 alone
is not sufficient.
C. BOTH statements TOGETHER are
sufficient, but NEITHER statement alone is sufficient.
D. EACH statement ALONE is
sufficient.
E. Statements 1
and 2 TOGETHER are NOT sufficient.
Q6) In
the adjacent figure , what is the length of segment BC?
(1) x = 900
(2)The perimeter of △ABC is 40.
Solution:
Using clue (1), applying
Pythagoras theorem at angle A,
BC2 = 122
+ 162 = 144 + 256 = 400 => BC = 20
Using clue (2),
Perimeter = AB + AC +
BC = 40 =>12 + 16 + BC = 40
=>BC = 40 - 28 = 12
As we could find the
solution independently with the clues (1) and (2),
Answer option is “D”
Q7) The diagonals of
a rhombus measure 24 and 10 units. Find the length of sides
of rhombus?
Solution:
In rhombus, diagonals
are at right angles and bisect each other.

AB2
= OA2 + OB2 = 122 + 52
= 144 + 25 =
169
=>AB = 13
Q8) The length and
width of a rectangle measure 24 and 18 units respectively.
Find radius of circle
circumscribing this rectangle?
Solution:
AC2 = AB2
+ BC2 = 242 + 182 = 576 + 324 = 900
AC = 30 units
AC is diameter of the
circle.
=> radius of circle = 30/2 = 15
units
Q9)
Find perimeter of
the given parallelogram?
Solution:
Applying Pythagoras theorem
at right angle ‘E’,
AD2 = DE2
+ AE2 = 32 + 42 = 9 + 16 = 25
AD = 5; BC = AD = 5
AB = CD = DE + EC =
3+5 = 8
Perimeter = AB + BC + CD + AD =
8+5+8+5 =26
Q10) John walked 6 m east
and then 8 m north. How far is he from his starting point?
solution:
Assume that John
started at A and walked 6 m east up to B and
then 8 m North up to
C.
Distance from the starting
point = AC
Applying Pythagoras at
right angle B,
AC2 = AB2
+ BC2 = 62 + 82 = 36+64 = 100
AC = 10 m
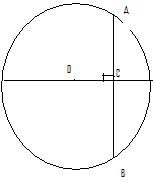
Q11)
Radius of the circle is 5 m and OC = 3 m. Find length of the chord AB?
Solution:
AO = radius = 5
Applying Pythagoras at
right angle C,
OA2 = OC2
+ AC2 =>AC2 = OA2 – OC2 = 52
- 32 = 25-9 = 16
=>AC = 4 =>AB = 2 AC = 8 m








Very good examples. Thanks Vemuri
ReplyDelete